From July 1, 2025, the process of acquiring Vietnamese citizenship has undergone significant changes under the revised Law on Vietnamese Nationality and accompanying regulations. If you’re a foreigner planning to become a Vietnamese citizen, understanding these updates is essential.
This guide will walk you through the latest requirements, eligibility conditions, application procedures, and what to expect during the naturalization process in Vietnam.

Table of Contents
Key Updates from July 1, 2025
Vietnam has made several important updates to its nationality law. Here are the key changes you should know:
- Online applications are now accepted: Applications can now be submitted online through the National Public Service Portal in addition to in-person submission at the Department of Justice.
- Stricter control on dual citizenship: New rules require applicants to clearly declare their current nationality and provide legal grounds if requesting to retain foreign citizenship.
- Stronger integration requirements: Applicants must now show stronger ties to Vietnam, such as long-term residence, employment, family relationships, or cultural/language familiarity.
- Simplified process for stateless individuals and ethnic Vietnamese overseas: Streamlined documentation and waived requirements for certain cases.
Who Can Apply for Vietnamese Citizenship?
Foreigners may apply for Vietnamese citizenship if they meet the following general conditions:
- Have full legal capacity under Vietnamese law, except for minors applying for Vietnamese citizenship together with their parent(s), or minors whose parent(s) are Vietnamese citizens;
- Abide by the Constitution and laws of Vietnam; respect the culture, traditions, customs, and practices of the Vietnamese people
- Speak Vietnamese adequately to integrate into the community;
- Currently reside permanently in Vietnam
- Have resided in Vietnam for at least 5 years continuously up to the date of application;
- Be capable of ensuring their livelihood in Vietnam;
- Have a name in Vietnamese or a language of an ethnic minority in Vietnam.
Exemptions:
- An applicant who has a spouse or biological child who is a Vietnamese citizen may be considered for exemptions from certain requirements (3, 5 and 6)
- Applicants who fall into one of the following categories may be considered for exemptions from certain requirements (3, 4, 5 and 6):
- Have a biological parent, or paternal/maternal grandparent who is a Vietnamese citizen;
- Have made special contributions to the cause of building and defending the Socialist Republic of Vietnam;
- Have made contributions to Vietnam;
- Be minors applying for Vietnamese citizenship together with their parent(s).
Required Documents for obtaining Vietnamese citizenship?
An application for Vietnamese citizenship typically includes:
- A completed application form (in Vietnamese)
- Certified copy of the passport and residence permit
- Birth certificate and criminal record from both Vietnam and the applicant’s home country
- Proof of Vietnamese language proficiency
- Proof of legal residence in Vietnam (e.g., lease, house ownership, or residency card)
- Employment certificate or income statement
- Statement of nationality renunciation or a commitment to do so
- Any documents supporting special circumstances (e.g., marriage certificate, Vietnamese relatives)
Note: All foreign documents must be legalized and translated into Vietnamese.
How to Apply for Vietnamese Citizenship
Here is the full process to obtain Vietnamese citizenship for foreigners:
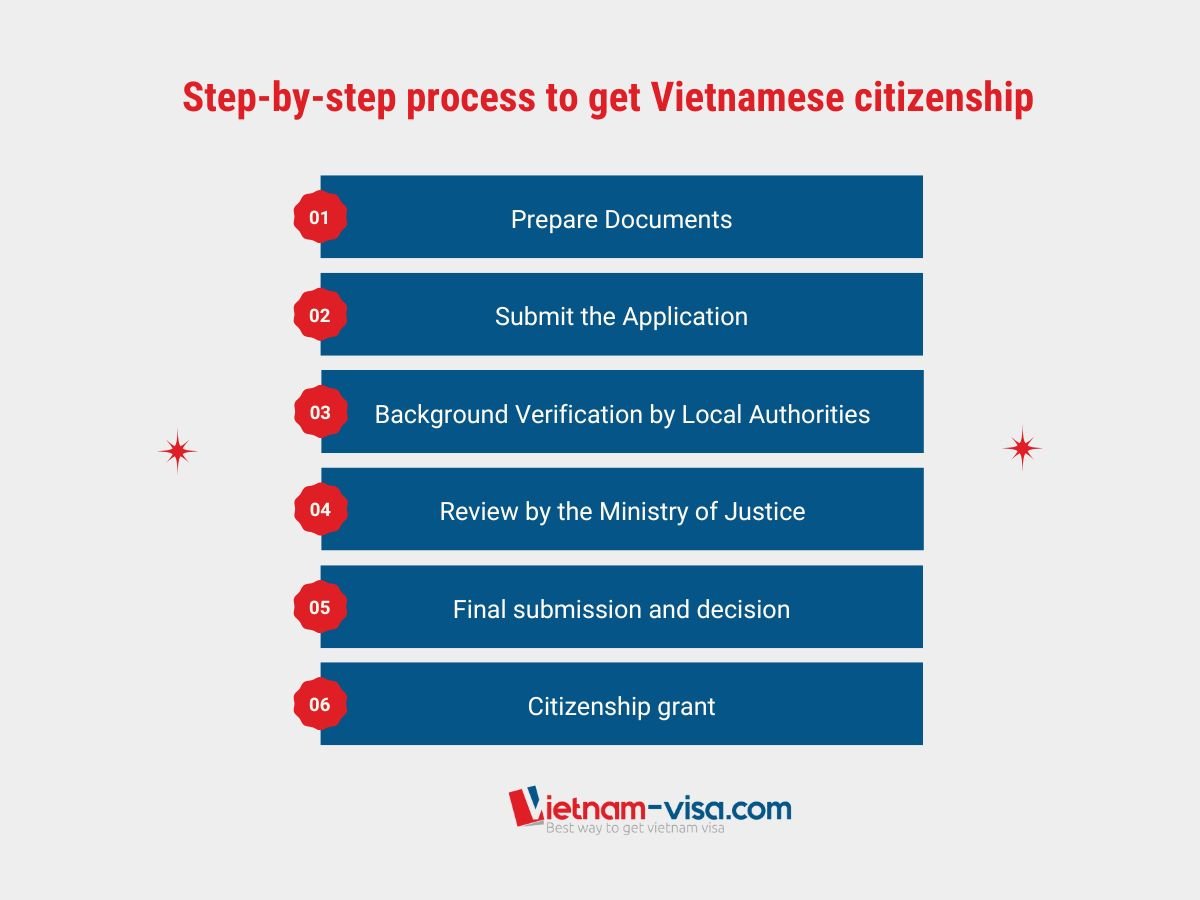
👉Step 1: Prepare your documents
First, the applicant must prepare full list of required documents with accurate content and format.
📌 Note: Missing or incorrect documents may result in requests for supplementation or even rejection of the application, leading to delays in processing.
👉Step 2: Submit your application
The completed application should be submitted to the Department of Justice in the province/city where the applicant is lawfully residing.
- Upon receiving the application:
- If the application is incomplete, the applicant will be notified to supplement the missing documents.
👉Step 3: Background Verification by Local Authorities
Within 5 working days of receiving a complete and valid application, the Department of Justice will send a written request to the Provincial Police to conduct background and identity verification of the applicant.
- The Provincial Police must complete the verification process within 30 working days;
- Meanwhile, the Department of Justice will review the submitted documents.
After receiving the verification results from the Police:
- Within 10 working days, the Department of Justice will finalize the application and submit it to the Chairperson of the Provincial People’s Committee;
- Within another 10 working days, the Chairperson will consider the application and send an official proposal to the Ministry of Justice.
👉Step 4: Review by the Ministry of Justice
Upon receiving the proposal from the Provincial People’s Committee, the Ministry of Justice will examine the application within 20 working days to assess whether the applicant fully meets the requirements.
If the conditions are met, the Ministry of Justice will notify the applicant to proceed with the renunciation of their current nationality, unless:
- The applicant is stateless, or
- The applicant requests to retain their current nationality and meets the conditions as stipulated by Vietnamese law.
👉Step 5: Final submission and decision
After receiving proof of nationality renunciation, the Minister of Justice will:
- Within 10 working days, report to the Prime Minister, who will submit the case to the President for issuance of a decision on Vietnamese citizenship.
If the applicant is stateless or has requested to retain their foreign nationality:
- The Ministry of Justice will finalize the application and directly report to the Prime Minister and President within 20 working days from the date of receiving the local authority’s proposal or verification result.
👉Step 6: Citizenship Grant
Once the President issues the Decision on naturalization:
- The Ministry of Justice will publish the Decision on its official website;
- Within 7 working days, the Ministry of Justice will forward the Decision to the Provincial People’s Committee where the applicant resides;
- The Provincial People’s Committee will then organize a ceremony to publicly announce and present the Decision on Vietnamese citizenship to the applicant.
Processing time may vary, but typically ranges from 4 to 6 months.
Special Cases: Retaining Foreign Citizenship
Under the revised law, applicants may request to retain their original nationality. This request must be justified with valid reasons, such as:
- Economic interests or family unity;
- Legal obstacles to renunciation in the home country;
- Special contributions to Vietnam.
These requests are reviewed on a case-by-case basis and require the President’s approval.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is based on our best understanding of the current Vietnamese laws and regulations as of July 2025. While we strive for accuracy and timely updates, we do not take legal responsibility for any outdated or incorrect information. For official advice, please consult with the relevant Vietnamese authorities or a qualified legal professional.